Overview: Discover how to evolve your workplace from a rigid command-and-control model to a thriving, collaborative work culture using the TIGERS 6 Principles. Learn how democracy and structured teamwork can revolutionize your organization’s culture, boosting productivity and engagement. Uncover the practical steps and tools, including the TIGERS Workforce Behavioral Profile™, which guides leaders in achieving sustainable transformation.

In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the stability of command-and-control work cultures are being increasingly scrutinized. As we progress through 2024, organizations are finding it challenging to maintain rigid hierarchical structures amidst the growing demand for agility and innovation.
Command-and-control work cultures, which have long relied on centralized decision-making and strict adherence to protocols, are struggling to adapt to the dynamic needs of modern workplaces. Today we explore the current state of these traditional work cultures and the factors driving the necessary shift towards more collaborative and democratic organizational models.
Autocracy and the command-and-control work culture share several similarities, such as centralized authority and limited employee input, which can stifle creativity and engagement. Both systems emphasize compliance over collaboration, resulting in a lack of innovation and flexibility. However, while these structures may have been effective in the past, they are increasingly incompatible with today’s workforce, which values participation and a sense of ownership. Understanding these similarities helps highlight the urgent need for transformation towards more inclusive and participatory work environments.
Workplace collaboration and democracy both emphasize participation and collective decision-making but differ in structure and scope. Collaboration in the workplace focuses on achieving specific organizational goals through teamwork and shared responsibilities, often facilitated by managers. In contrast, democracy involves equal voting rights and aims to represent diverse interests within a larger societal framework. Bridging the gaps between these two concepts in the human mindset requires a focus on open communication, shared leadership, and civic engagement. By fostering these elements, organizations can create a more cohesive and motivated workforce, aligning closer with democratic principles.
Stability of Command-and-Control Work Cultures in 2024
In 2024, command and control work cultures face decreasing stability due to three key factors that are driving both culture awareness and change.
The first is technological advancement. The rise of digital tools and remote work technologies promote a more interconnected and collaborative work environment, making rigid hierarchical structures less effective. These new technologies break down geographical barriers and establish seamless communication and collaboration across the globe. With tools like video conferencing, cloud-based project management, and real-time collaboration software, teams can work together efficiently regardless of their physical locations. This connectivity allows for a diverse range of ideas and perspectives, enhancing creativity and problem-solving capabilities. Additionally, remote work technologies offer flexibility, improving work-life balance and employee satisfaction, which in turn boosts productivity and fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. By integrating these digital tools, organizations can create a dynamic and inclusive work environment that leverages the collective intelligence of a global workforce.
The second is Employee Expectation. Modern employees, especially Millennials and Gen Z age groups, demand more autonomy, flexibility, and opportunities for input. These demands are incompatible with strict command and control cultures. Members of these age groups have also been schooled in working on teams to deliver school projects, which prepares them for today’s modern workforce. The alarm facing command and control leaders today is who to employ if their employment pipeline shrinks more than it already has from problems with talent retention.
The third is Innovation. Innovation requires agile and innovative solutions that thrive in collaborative work environments. These environments nurture the rapid exchange of ideas and quick adaptation to changing circumstances. In a collaborative setting, diverse teams can brainstorm and debate concepts, combining their unique skills and perspectives to tackle complex problems more effectively. This dynamic approach accelerates the innovation process, allowing organizations to stay ahead in competitive markets.
Therefore, transitioning to more collaborative operations involves embracing these trends to create adaptable and resilient organizations.
Autocracy and the command-and-control work culture share several similarities
With autocracy becoming vilified in the US political environment, there is an increasing rejection of the autocratic mindset. That said, there are four critical areas that impact the workforce today.
The first is Centralized Decision-Making. In both systems, decisions are made by a single leader or a small group of leaders without input from others. Decisions like these often result in poor decisions due to a lack of diverse perspectives and critical feedback. When decision-making is concentrated in the hands of a few, it is prone to biases, blind spots, and groupthink, where dissenting opinions are suppressed, and alternative viewpoints are overlooked. This insular approach often leads to a narrow understanding of complex issues and suboptimal solutions that fail to address the needs and concerns of all stakeholders.
The second is Limited Input. Employees or citizens have little to no say in decisions, leading to a lack of engagement and talent loss which shrinks the employment funnel. It also makes organizations less productive and profitable.
The third is Strict Hierarchy: A clear top-down structure exists, with those at the top holding most of the power and authority. This often results in mediocrity because it stifles innovation, discourages employee engagement, and limits the flow of ideas. In such environments, decisions are made by a select few, often without input from those who are directly involved in day-to-day operations or who have unique insights into customer needs and market trends. This can lead to outdated or out-of-touch strategies that fail to capitalize on new opportunities or address emerging challenges effectively. Furthermore, employees in lower ranks may feel undervalued and disempowered, reducing their motivation to contribute creatively or go above and beyond in their roles. Employees often do just enough to skate by.
The final reason is Compliance over Collaboration. An emphasis on obedience and following orders bores Millennials and Gen Z employees because it stifles their need for creativity, autonomy, and meaningful work. These generations value workplaces that offer opportunities for innovation, personal growth, and a sense of purpose. They thrive in environments where their voices are heard, and their ideas can contribute to the organization’s success. Rigid hierarchies and a focus on strict adherence to orders fail to leverage their digital fluency, adaptability, and collaborative skills.
These similarities highlight how both systems can suppress individual initiative and collective input, leading to less dynamic and adaptable environments.
Collaborative work culture and democracy also share several similarities.
Collaborative work culture and democracy share several similarities, both emphasizing the importance of participation, equality, and collective decision-making. In a democratic system, every person has a voice and the opportunity to contribute to the direction of their community or nation. Mirroring this, workplace collaboration invites input and engagement from all team members. Both systems rely on open communication, mutual respect, and shared responsibility to function effectively. This inclusive approach fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a more cohesive environment.
While workplace collaboration and democracy both emphasize participation and collective decision-making, they differ in structure and scope. Workplace collaboration is often directed towards achieving specific organizational goals and is usually overseen by managers who guide and facilitate the process. Decisions are often influenced by employee input with final decisions being made transparently by leaders with expertise. In contrast, democracy operates on the principle of equal voting rights for all citizens, regardless of their expertise, with the aim of representing diverse interests in governance. Democratic decisions are made through voting and are intended to serve the broader public interest, beyond specific organizational objectives.
How to bridge the gaps between collaborative work culture and democracy in the human mindset
There are three key activities to focus on that bridge the gap between collaborative work culture and democracy. The first is cultivating open communication. Leaders who encourage transparent dialogue where all voices are heard and respected build a work environment of mutual trust and understanding.
The second is promoting shared leadership. Organizations that train and develop employees with decision-making and team facilitation skills can distribute leadership roles and decision-making responsibilities. This empowers employees with certain strengths that are appropriate to the task at hand. This blending of hierarchical and egalitarian approaches adds interest for employees, develops talent and widens the bench for succession leadership and the next generation of leaders.
The third is encouraging civic engagement. Educate employees on the importance of their contributions both in the workplace and in democratic processes. This gives employees leadership experience and highlights the value of active participation and responsibility in both realms.
By integrating these principles, both employees and leaders can better appreciate the parallels and distinct needs of effective collaboration and democratic participation.
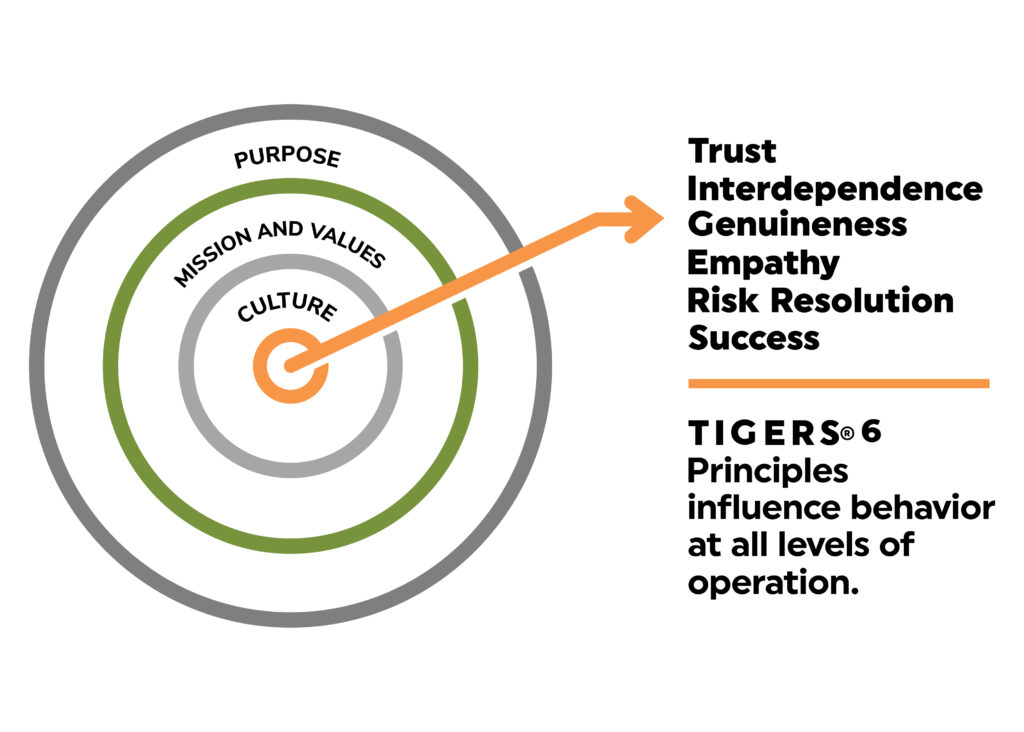
Measuring the transition from command-and-control with the TIGERS 6 Principles Workforce Behavioral Profile™
The TIGERS 6 Principles, responsible for building high performance teams and leaders, are trust, interdependence, genuineness, empathy, risk resolution and success. Anchored by behaviors, a six TIGERS Principles overview includes the following:
Trust: Encourages openness and transparency, shifting from rigid oversight to mutual respect and reliability.
Interdependence: Fosters teamwork and shared goals, moving away from isolated decision-making to collaborative efforts.
Genuineness: Promotes authenticity and honest communication, replacing top-down directives with sincere interactions.
Empathy: Enhances understanding and consideration among team members, reducing hierarchical barriers and fostering a supportive environment.
Risk: Supports calculated risk-taking and innovation, encouraging input from all levels rather than stifling creativity. Effective problem-solving, decision-making and organizational learning are predictable outcomes.
Success: Creates a shared vision of achievement, aligning individual and team goals with organizational objectives in a way that is very satisfying and stimulating for employees.
Integrating these principles with employee endorsed behaviors aligns with modern employees’ values, ensuring buy-in and participation by everyone when leaders hire correctly. Providing training on these principles equips leaders and employees with the necessary skills for collaboration. Education on the TIGERS 6 Principles and conversations about them allows for ease of adaptation and minimizes resistance, making the transformation smoother and more sustainable.
The TIGERS Workforce Behavioral Profile™ with its three surveys for the same group plays a critical role in this transformation by the following:
- Benchmarking: The assessment establishes a baseline for current team dynamics and identifies areas for improvement.
- Tracking Progress: Regular surveys after training and interventions help leaders monitor changes and improvements in behavior over time. This ensures that the integration of TIGERS principles is effective.
- Guiding Adjustments: Just in time adjustments provide leaders with actionable insights to make informed decisions on what is next. It fosters continuous growth and alignment with organizational goals.
By using the TIGERS Workforce Behavioral Profile and the three surveys for the same group, leaders can systematically guide their teams through the transformation from a command-and-control culture to a more collaborative and innovative environment.
To learn more about the TIGERS Workforce Behavioral Profile to unlock the potential of your team, there is a complimentary webinar available to view. Discover how to transform your workplace culture from command-and-control to collaboration using the TIGERS 6 Principles. Learn how the three surveys help leaders track behavioral changes and drive continuous improvement. Don’t miss this opportunity to gain actionable insights and practical tools for fostering a collaborative, high-performing work environment. Sign up now to elevate your understanding and discover how this tool empowers teams.
For more details and to register, visit TIGERS Workforce Behavioral Profile Webinar.
Copyright TIGERS Success Series, Inc. by Dianne Crampton

The TIGERS 6 Principles empower Executives and Consultants with a comprehensive collaborative work culture and leadership platform to resolve avoidable talent, engagement and work community problems that stunt growth.
A researched and validated collaborative work culture and facilitative leadership model, licensing is available for HR Executives, Operations and Project Managers, Consultants and Coaches to improve their operations and client success.
Schedule a call to secure a tour of the comprehensive TIGERS 6 Principles system.